-->
- Outlook 2016 Stuck In Sending Mail
- Outlook 2016 Stuck In Send And Receive
- Outlook 2016 Stuck In Sending Data
Original KB number: 2652320
Symptoms
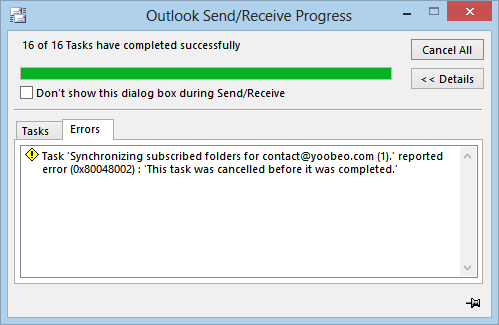
When you open a file or send an email message in Microsoft Outlook 2010 or later versions, Outlook freezes, or you receive the following error message:
In Windows 7, choose Start, and in the Search programs and files box, type Outlook /safe, and then press Enter. In Windows 8, on the Apps menu, choose Run, type Outlook /safe, and then choose OK. Close Outlook, and then open it normally. If Outlook isn't stuck at a screen that says 'Processing,' or this didn't resolve your issue, continue to. Fix Outlook Not Sending Emails in Outlook for Mac 2016 In the Mac version of Outlook, there are a few things you can try to get Outlook working again. Double-check Recipient's Email.
Outlook not responding
Cause
This problem occurs for one or more of the following reasons:
- You have not installed the latest updates.
- Outlook is in use by another process.
- Outlook is loading external content, such as images in an email message.
- A previously installed add-in is interfering with Outlook.
- Your mailboxes are too large.
- Your AppData folder is redirected to a network location.
- You have to repair your Office programs.
- Outlook data files have become corrupted or damaged.
- Your installed antivirus software is outdated, or it conflicts with Outlook.
- Your user profile has become corrupted.
- Another program conflicts with Outlook.
Note
- This issue may occur for one or more of the reasons in this section. To fix this issue, you may have to follow the troubleshooting steps in the Resolution section.
- Many of these items can be automatically checked by the Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant (SaRA). To start the automated checks, follow these steps:
- Install the Outlook Advanced Diagnostics tool.
- Select Run when you are prompted by your browser.
- In the report that's generated, review the items on the Issues found tab. For configuration details about Outlook, Windows, and your computer, review the settings on the Detailed View tab.
Resolution
To resolve this problem, make sure that your computer meets the Outlook 2016 system requirements, Outlook 2013 system requirements or Outlook 2010 system requirements.
Note
These steps are provided in a specific order based on commonality and complexity. Follow these steps in the given order.
Step 1 - Install the latest updates
The Office installation on your computer might not be up to date. This might be because Windows Update is not configured on your computer to automatically download and install recommended updates. By installing important, recommended, and optional updates, you can often correct problems by replacing out-of-date files and fixing vulnerabilities. To install the latest Office updates, click the link for your version of Windows, and then follow the steps in the article:
Make sure that the latest updates for Outlook are installed. For more information, see How to install the latest applicable updates for Microsoft Outlook (US English only).
Step 2 - Make sure that Outlook is not in use by another process
Performance may be decreased if you use the Outlook AutoArchive feature or sync to Outlook with a mobile device. This is because these processes can use a large number of resources.
If Outlook is in use by another process, this information is displayed in the status bar at the bottom of the screen. If you try to perform other actions while Outlook is in use, Outlook may not respond. Let the task in process finish its job before you try another action.
Step 3 - Check the problem caused by external content
To resolve this issue, use one of the following methods:
- Prevent Outlook to download external contents. To do this, go to File > Options > Trust Center > Automatic Download, select the following two options:
- Don't download pictures or other content automatically in HTML e-mail option.
- Warn me before downloading content when editing, forwarding, or replying e-mail.
- Avoid sending such an email with external source.
Step 4 - Investigate possible add-in issues
Although add-ins can enhance your user experience, they can occasionally interfere or conflict with Outlook. Try to start Outlook without any add-ins running.
How to start Outlook without add-ins
- Do the following, as appropriate for your operating system:
- If you are running Windows 8, swipe in from the right edge of the screen, and then tap Search. (If you are using a mouse, point to the upper-right corner of the screen, move the mouse pointer down, and then select Search.) Type Run in the search box, and then tap or select Run.
- If you are running Windows 10, Windows 7 or Windows Vista, select Start.
- If you are running Windows XP, select Start, and then select Run.
- Type Outlook.exe /safe, and then select OK.
- If the problem is resolved, select Options on the File menu, and then select Add-Ins.
- Select COM Add-ins, and then select Go.
- Clear all the check boxes in the list, and then select OK.
- Restart Outlook.
If the problem does not occur after you restart Outlook, one of the add-ins is likely the cause of the problem. Restore the add-ins one at a time until the problem does occur to determine which add-in is causing the problem.
Step 5 - Check whether your mailbox is too large
As your mailbox size increases, more resources are required to open each folder. If you have a large number of items in any single folder, you may experience performance issues during certain operations. For more information, see Outlook performance issues when there are too many items or folders in a cached mode .ost or .pst file.
We recommend that you move several items in your larger folders to separate folders, or that you archive those items by using the AutoArchive feature.
How to create a folder
On the Folder tab, select New Folder in the New group.
In the Name box, enter a name for the folder.
In the Select where to place the folder list, select the location for the new folder.
Note
The new folder will become a subfolder of the folder you select.
Select OK.
To manage your mailbox by reducing the size of the Outlook data file, see Reduce the size of Outlook Data Files (.pst and .ost).
To manage your mailbox by using the AutoArchive feature, see AutoArchive settings explained.
Step 6 - Check whether your AppData folder is being redirected to a network location
Outlook stores certain data, such as email signatures and the spelling checker dictionary, in the AppData folder. If the network is performing slowly, Outlook must wait for read and write operations to the AppData directory to finish.
How to disable redirection of the AppData directory
Exit Outlook.
Start Registry Editor. To do this, use one of the following procedures, as appropriate for your version of Windows:
- Windows 10 or Windows 8: Press Windows Key+R to open a Run dialog box. Type regedit.exe and then press OK.
- Windows 7: Select Start, type regedit.exe in the search box, and then press Enter.
In Registry Editor, locate and then select the following subkey:
HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionExplorerUser Shell FoldersLocate and then double-click the AppData value.
In the Value data box, type the following path, and then select OK:
%USERPROFILE%AppDataRoamingExit Registry Editor.
Step 7 - Repair Office programs
You can automatically repair your Office program files to resolve such problems as Outlook freezing or not responding.
How to automatically repair Office
- Exit any Microsoft Office programs that are running.
- Open Control Panel, and then open the Add or Remove Programs item (if you are running Windows XP) or Programs and Features (if you are running Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, or Windows Vista).
- In the list of installed programs, right-click Microsoft Office 2016, Microsoft Office 2013 or Microsoft Office 2010, and then select Repair.
Step 8 - Repair Outlook data files
When you install Outlook, an Inbox repair tool (scanpst.exe) is also installed on your PC. The Inbox repair tool can resolve problems by scanning your Outlook data files, and repairing errors. To use the Inbox repair tool, exit Outlook, and then follow the steps in Repair Outlook Data Files (.pst and .ost).
Step 9 - Check whether antivirus software is up-to-date or conflicts with Outlook
If your antivirus software is not up-to-date, Outlook may not function correctly.
How to check whether antivirus software is up to date
To keep up with new viruses as they are created, antivirus software vendors periodically provide updates that you can download from the Internet. Download the latest updates by visiting your antivirus software vendor's website.
For a list of antivirus software vendors, see Consumer antivirus software providers for Windows.
How to check whether antivirus software conflicts with Outlook
If your antivirus software includes integration with Outlook, you may experience performance issues. You can disable all Outlook integration within the antivirus software. Or, you can disable any antivirus software add-ins that are installed in Outlook.
Important
When you change your antivirus settings, this may make your PC vulnerable to viral, fraudulent, or malicious attacks. We do not recommend that you try to change your antivirus settings. Use this workaround at your own risk.
You may have to contact your antivirus software vendor to determine how to configure the software to exclude any integration with Outlook or to exclude scanning in Outlook.
Note
If you also plan to perform file-level virus scanning of .pst, .ost, Offline Address Book (.oab), or other Outlook files while Outlook is in use, see Plan antivirus scanning for Outlook 2010 or Planning considerations for deploying Outlook 2016 for Windows.
Step 10 - Create a user profile in Outlook
To create a user profile, follow these steps:
In Control Panel, select Programs, select User Accounts, and then select Mail to open Mail items.
Select Show Profiles.
Select the profile that you want to remove, and then select Remove.
Select Add.
In the Profile Name dialog box, type a name for the profile.
Specify the user name, the primary SMTP address, and the password. Then, select Next.
You may receive the following prompt:
Allow this website to configure <alias@domain server> settings?In this prompt, select the Don't ask me about this again checkbox, and then select Allow.
Step 11 - Perform a Selective Startup (advanced users)
When you start Windows normally, several applications and services start automatically and then run in the background. These applications and services can interfere with Outlook. A Selective Startup or 'clean boot' process can help you identify problems that are caused by application conflicts.
If you use the Selective Startup option in System Configuration, you can turn services and startup programs on or off individually to check whether the problem occurs the next time that you start your computer. In System Configuration, if you select a check box, the related service or startup program runs when you restart the computer. If the check box is cleared, the service or startup program does not run when you restart the computer.
Follow this procedure to use the process of elimination to identify the problem in Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, or Windows Vista.
Note
For more information about performing a clean boot, see How to perform a clean boot in Windows.
How to do a Selective startup
In Control Panel, select System and Security, select Administrative Tools, and then double-click System Configuration.
Note
If you are prompted for an administrator password or for confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
Select the General tab, select Selective startup, and then clear the Load system services and the Load startup items check boxes.
Select the Load system services check box, select OK, and then select Restart.
If the problem reoccurs after you restart the computer, do one or both of the following tasks, as necessary.
To determine which system service is causing the problem
In System Configuration, select the Services tab, select Disable all, select the check box for the first service that is listed, and then restart the computer.
Note
If the problem doesn't reoccur, then you can eliminate the first service as the cause of the problem.
With the first service selected, select the second service check box, and then restart the computer.
Repeat this process until you reproduce the problem.
Note
If you can't reproduce the problem, you can eliminate system services as the cause of the problem.
To determine which startup item is causing the problem
In System Configuration, select the General tab, and then select the Load startup items check box.
Select the Startup tab, select Disable all, select the check box for the first startup item that is listed, and then restart the computer.
Note
If the problem doesn't reoccur, you can eliminate the first startup item as the cause of the problem.
While the first startup item is selected, select the second startup item check box, and then restart the computer. Repeat this process until you reproduce the problem.
Step 12 - Create a Windows user profile (advanced users)
Your user profile is a collection of settings that let you customize the computer appearance and performance. It contains settings for desktop backgrounds, screen savers, sound settings, and other features. User profiles help make sure that your personal preferences are used when you log on to Windows.
To determine whether this problem is caused by a corrupted user profile, create a user profile to see whether the problem still occurs when you use the new profile.
How to repair a corrupted user profile in Windows 8
Step 1 - Create a user account
To create a user profile, you must first create a user account. When the new account is created, a profile is also created.
Swipe in from the right edge of the screen, and then tap Search. (If you are using a mouse, point to the upper-right corner of the screen, move the mouse pointer down, and then select Search.) Type Command Prompt in the search box, right-click Command Prompt, and then select Run as administrator.
Note
If you're prompted for an administrator password or for confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
Type net user UsernamePassword /add, and then press Enter.
Step 2 - Copy old files to the new user profile** After you create the profile, you can copy the files from the existing profile
Note
You must have at least three user accounts on the computer to complete these steps. This includes the new account you just created.
Log on as a user other than the user that you just created or the user that you want to copy files from.
In Control Panel, select Appearance and Personalization, and then select Folder Options.
Select the View tab, and then select Show hidden files, folders, and drives.
Clear the Hide protected operating system files check box, select Yes to confirm, and then select OK.
Open File Explorer. To do this, Swipe in from the right edge of the screen, and then tap Search. (If you are using a mouse, point to the upper-right corner of the screen, move the mouse pointer down, and then select Search.) Enter File Explorer in the search box, tap or select Apps, and then tap or select File Explorer. Type Command Prompt in the search box, right-click Command Prompt, and then select Run as administrator.
Locate the C:UsersOld_Username folder, in which C is the drive that Windows is installed on, and Old_Username is the name of the profile that you want to copy files from.
Select all the files and folders in this folder, except the following files:
- Ntuser.dat
- Ntuser.dat.log
- Ntuser.ini
On the Edit menu, select Copy.
Locate the C:UsersNew_Username folder, in which C is the drive that Windows is installed on, and New_Username is the name of the user profile that you created earlier in this method.
On the Edit menu, select Paste.
Log off, and then log back on as the new user.
Note
If you have email messages in an email program, you must import your email messages and addresses to the new user profile before you delete the old profile. If everything is working correctly, you can now delete the old profile.
Next step
If the information in this article does not help resolve your problem in Outlook 2016, Outlook 2013 or Outlook 2010, see the following resources for more information:
References
-->Symptoms
In Outlook for Microsoft 365, Microsoft Outlook 2016, or Microsoft Outlook 2013, you experience one or more of the following symptoms:
New email messages aren't received.
When you try to send an email message, it isn't sent. Instead, it remains in the Outbox.
When you try to configure a new Outlook profile by using an IMAP account, you receive the following error message:
Internal MAPI error: The profile does not contain the requested service. Contact your administrator.
When you select File in Outlook 2016, the following warning messages are displayed:
Metered Connection Warning
We noticed the metered connection you're on may charge extra and this Office program might access online content. You may want to:- Tap or click the network icon and turn on Airplane mode to go offline
- Connect to a WiFi or LAN network that isn't metered
- Check the status of your data plan with your mobile operator
Upgrade in Progress
Your mailbox is currently being optimized as part of an upgrade to Outlook 2016. This one-time process may take more than 15 minutes to finish, and performance may be affected while the optimization is in progress.
Resolution
To fix these issues for Outlook for Microsoft 365, update your Office installation to version 2008 (Build 13127.20508) or a later version.
- Open any Office application, such as Outlook or Word.
- Select File, and then select Office Account or Account.
- Check the version number that is listed under Office Updates. If the version is earlier than 2008, select Update Options, and then select Update Now.
For more information about update channels for Office 365 clients, see Update history for Microsoft 365 Apps (listed by date).
If updating the Office installation does not fix the issues, use one of the methods that are listed in the 'Workaround' section.
There is no resolution for Outlook 2016 and Outlook 2013 at this time. Use the appropriate workarounds for these products.
Workaround
For Outlook for Microsoft 365 and Outlook 2016
To work around these issues, try Method 1 first. If that doesn't fix the issues, try Method 2.
Method 1: Delete the SecurityManager key in the registry
The issues might be caused by the registry values under this subkey:
HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftOfficeClickToRunREGISTRYMACHINESoftwareMicrosoftSecurityManagerCapAuthzApplicationsEx
Delete the SecurityManager key and its subkeys in the registry.
Important
Follow the steps in this section carefully. Serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Before you modify it, back up the registry for restoration in case problems occur.
Exit Outlook.
Start Registry Editor.
- For Windows 10, Windows 8.1, and Windows 8: Press Windows logo key+R to open a Run dialog box. Type regedit.exe, and then select OK.
- For Windows 7: Select Start, type regedit.exe in the search box, and then press Enter.
In Registry Editor, locate the following subkey in the registry:
HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftOfficeClickToRunREGISTRYMACHINESoftwareMicrosoftSecurityManagerCapAuthzApplicationsExRight-click the SecurityManager key, and select Permissions.
Select Advanced, and select the Replace all child object permission entries with inheritable permission entries from this object check box.
Select OK.
Select yes if you receive the following notification: 'This will replace explicitly defined permissions on all descendants of this object with inheritable permissions from <parent key>. Do you wish to continue?
Select OK.
Right-click the SecurityManager key, and select Delete to delete the SecurityManager key and the subkeys.
Exit Registry Editor.
Repair the Office application, and check whether the issues have been resolved.
Method 2: Stop third-party applications that access MAPISVC.inf file
These issues may also be caused by third-party applications that access MAPISVC.inf and prevent Outlook from setting up the Account Manager. To mitigate this situation, stop the applications and processes that may be affecting MAPISVC.inf.
Use Process Monitor to see the processes that are accessing MAPISVC.inf. If a process displays a SHARING_VIOLATION on MAPISVC.inf, it indicates that the associated application is likely to be responsible for the issues. For instance, RepMgr.exe (C:Program FilesConferRepMgr.exe) is an application that is known to cause these issues. Stop this process if you see it in Process Monitor.
Third-party information disclaimer
The third-party products that this article discusses are manufactured by companies that are independent of Microsoft. Microsoft makes no warranty, implied or otherwise, about the performance or reliability of these products.
For Outlook 2013
To work around these issues, try Method 1 first. If that doesn't fix the issues, try Method 2.
Method 1: Verify permissions in the registry
In some cases, the issues are related to a permissions issue in the registry. To determine whether this is the cause of the issues and then fix them, follow these steps:
Exit Outlook.
Start Registry Editor.
- For Windows 10, Windows 8.1 and Windows 8: Press Windows logo key+R to open a Run dialog box. Type regedit.exe, and then select OK.
- For Windows 7: Select Start, type regedit.exe in the search box, and then press Enter.
In Registry Editor, locate and right-click the following subkey in the registry, and then select Permissions:
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOTInstallerComponentsF1291BD604B860441AB89E60BDEE0F9CUnder Group or user names, find your own user name or a group that you're a member of (such as Users or Administrators).
If you're unsure about which groups your user account is a member of, follow these steps:
Open Control Panel.
From Category view, select User Accounts, and then select User Accounts again.
Select Manage User Accounts.
In the User Accounts window, find your User Name, and review the groups that are listed in the Group column.
Note
You may have to expand the Group column to view all the groups.
When you are finished, select Cancel.
If you do not see a group that you're a member of or your own user name listed in the permissions list, select Add, and then add your own user account.
Select OK.
Select your user name or the group that you're a member of.
View the permissions for your user name or group, and make sure that the Read permission has Allow selected.
Select OK.
Exit Registry Editor.
Method 2: Run a repair of Office
Follow the steps in the following article to repair your Office installation. This method is most appropriate for MSI-based installations of Office. To determine whether your Office installation is Click-to-Run or MSI-based, see the 'More information' section.
Outlook 2016 Stuck In Sending Mail
More information
Outlook 2016 Stuck In Send And Receive
To determine whether your Office installation is Click-to-Run or MSI-based, follow these steps:
Outlook 2016 Stuck In Sending Data
- Start Outlook.
- On the File menu, select Office Account.
- An Update Options item is displayed for Office Click-to-Run installations, but not for MSI-based installations.