- Windows 10 Remote Desktop Loses Connection
- Windows Remote Desktop Loses Connection
- Microsoft Remote Desktop Losing Connection
- Microsoft Remote Desktop Mac Connection Lost
To show the Remote Desktop Session Collection you will need to make a change to the Registry. HKLM SOFTWARE Microsoft Windows NT CurrentVersion Terminal Server CentralPublishedResources PublishedFarms RemoteDesktops. To show the Desktop Session Icon, Change the value (ShowInPortal) to 1 from 0. Configuring remote PC'. Then the computer connects but I cannot use it before it looses connection again and thus it gets stuck in an endless loop.This happens whenever I am connected on a MacOS to my office PC desktop on Windows 10, via Pulse and Microsoft Remote Desktop as per my organization's settings. We have a client with a remote desktop server with users connecting internally and a few externally. The main user connecting externally experiences frequent drops but it then automatically reconnects after a few tries. We would like to figure out if this is an issue on the user's end or at the remote desktop server's end. To sum up, if you have previously not configured Remote Desktop, or have set RDP to 'Deny', and then you set it to 'Enabled' with a GPO, then during the Group Policy updates the settings will briefly revert back to the local settings on the machine before being updated to the current Group Policy.
After Remote Desktop client loses its connection to the remote desktop, the client can't immediately reconnect. The user receives one of the following error messages:
Windows 10 Remote Desktop Loses Connection
- The client couldn't connect to the terminal server because of a security error. Make sure you are signed in to the network, then try connecting again.
- Remote Desktop disconnected. Because of a security error, the client could not connect to the remote computer. Verify that you are logged onto the network and then try connecting again.
When the Remote Desktop client reconnects, the RDSH server reconnects the client to a new session instead of the original session. However, when you check the RDSH server, it says that the original session is still active and didn't enter a disconnected state.
To work around this issue, you can enable the Configure keep-alive connection interval policy in the Computer ConfigurationAdministrative TemplatesWindows ComponentsRemote Desktop ServicesRemote Desktop Session HostConnections group policy folder. If you enable this policy, you must enter a keep-alive interval. The keep-alive interval determines how often, in minutes, the server checks the session state.
This issue can also be fixed by reconfiguring your authentication and configuration settings. You can reconfigure these settings at either the server level or by using group policy objects (GPOs). Here's how to reconfigure your settings: Computer ConfigurationAdministrative TemplatesWindows ComponentsRemote Desktop ServicesRemote Desktop Session HostSecurity group policy folder.
- On the RD Session Host server, open Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration.
- Under Connections, right-click the name of the connection, then select Properties.
- In the Properties dialog box for the connection, on the General tab, in Security layer, select a security method.
- Go to Encryption level and select the level you want. You can select Low, Client Compatible, High, or FIPS Compliant.
Windows Remote Desktop Loses Connection
Note
Microsoft Remote Desktop Losing Connection
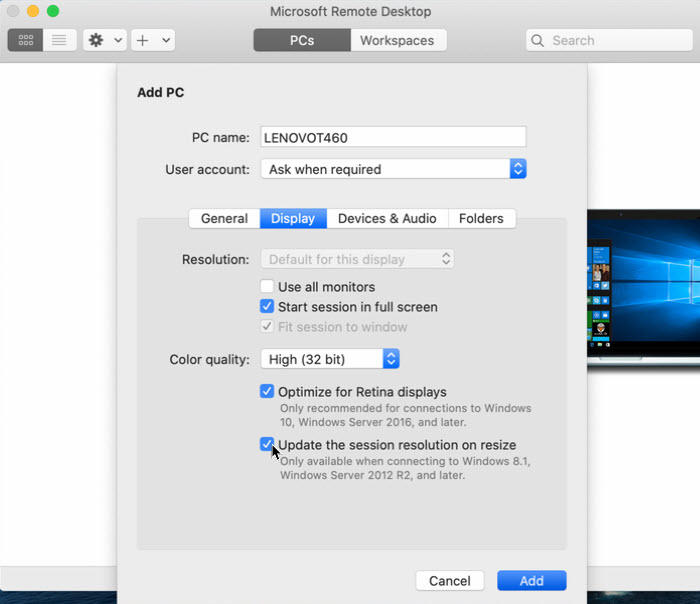
Microsoft Remote Desktop Mac Connection Lost
- When communications between clients and RD Session Host servers require the highest level of encryption, use FIPS-compliant encryption.
- Any encryption level settings you configure in Group Policy override the settings you configured using the Remote Desktop Services Configuration tool. Also, if you enable the System cryptography: Use FIPS compliant algorithms for encryption, hashing, and signing policy, this setting overrides the Set client connection encryption level policy. The system cryptography policy is in the Computer ConfigurationWindows SettingsSecurity SettingsLocal PoliciesSecurity Options folder.
- When you change the encryption level, the new encryption level takes effect the next time a user signs in. If you require multiple levels of encryption on one server, install multiple network adapters and configure each adapter separately.
- To verify your certificate has a corresponding private key, go to Remote Desktop Services Configuration, right-click the connection that you want to view the certificate for, select General, then select Edit. After that, select View certificate. When you go to the General tab, you should see the statement, 'You have a private key that corresponds to this certificate' if there's a key. You can also view this information with the Certificates snap-in.
- FIPS-compliant encryption (the System cryptography: Use FIPS compliant algorithms for encryption, hashing, and signing policy or the FIPS Compliant setting in Remote Desktop Server Configuration) encrypts and decrypts data sent between the server and client with the Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 140-1 encryption algorithms that use Microsoft cryptographic modules. For more information, see FIPS 140 Validation.
- The High setting encrypts data sent between the server and client by using strong 128-bit encryption.
- The Client Compatible setting encrypts data sent between the client and the server at the maximum key strength supported by the client.
- The Low setting encrypts data sent from the client to the server using 56-bit encryption.